Weekly Market Commentary
U.S. economic growth in the third quarter accelerated sharply, growing at an annual pace of 4.9%, according to last month’s report by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis.
But GDP (Gross Domestic Product) data are backward-looking. It’s a snapshot from July through September. We’re well into November.
An early estimate from the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow model shows GDP tracking at a modest 2.1% as of November 8th.
Last week, we reviewed trends in the unemployment rate, which remains just below 4% (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics) but has ticked off the bottom.
This week let’s look at another data point in the labor market. Continuing jobless claims are released weekly by the Department of Labor. When someone is laid off from work, they have the option to file for unemployment insurance through their state’s labor department.
Most states require that you file weekly or biweekly, documenting your job search in order to receive regular benefits. Most states pay benefits for 6 months.
It is easier to secure work when firms are hiring, so it is not a surprise that the number of people receiving jobless benefits is low before a recession begins. During the depth of a recession, fewer companies are hiring, layoffs are high, and job searches can be challenging and lengthy.
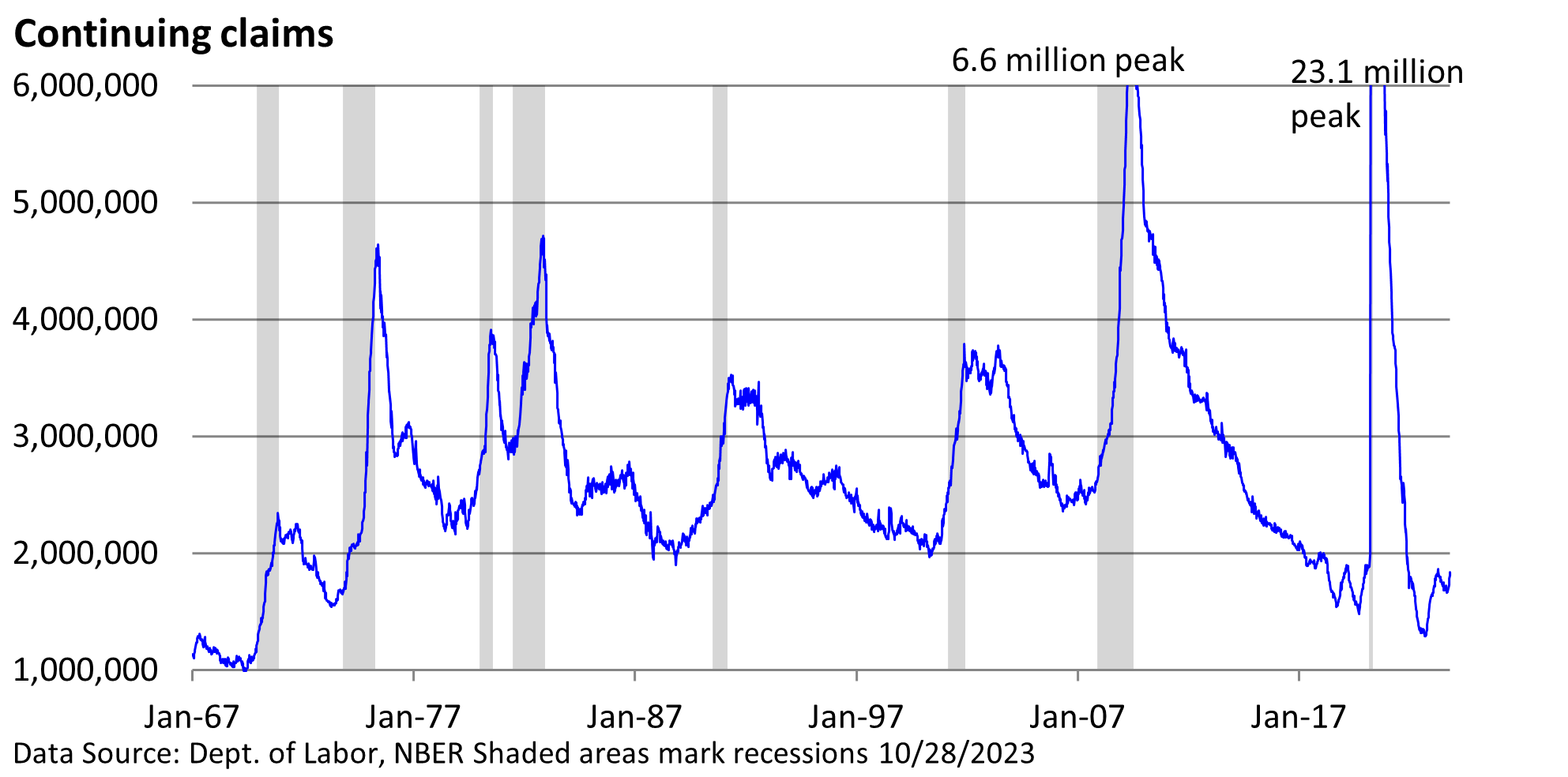
As illustrated by the graphic, continuing claims are currently low but have turned higher.
Based on 50 years of data, an increase of this magnitude has always led to a recession. On average, a recession starts within 11 months of the lowest point in continuing claims, but the range is wide: 4 to 21 months.
Perhaps we’ll take a path similar to the mid-1980s when claims rose for 2 years before heading lower. Due to the pandemic and government cash payments, the economic cycle has been distorted, and forecasting models have been disrupted.
This cycle’s most recent low was September 2022. At a minimum, the increase in continuing claims points to a moderation in economic growth. It’s not all industries, but on average, it is taking a little bit longer for the unemployed to secure employment.




