Weekly Market Commentary
In the past, investors paid close attention to the monthly employment report. Today the focus has shifted to the CPI. Blame high inflation for the jump in interest rates, which has pressured the major stock market averages.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that while inflation eased in April, it remains high.
The monthly rate of increase for the Consumer Price Index (CPI) was 0.4% in April. On an annual basis, it slowed from 5.0% in March to 4.9% in April. The core CPI, which excludes food and energy, also rose 0.4%. It eased from an annual rate of 5.6% to 5.5%.
Both readings are well above the Fed’s 2% annual target.
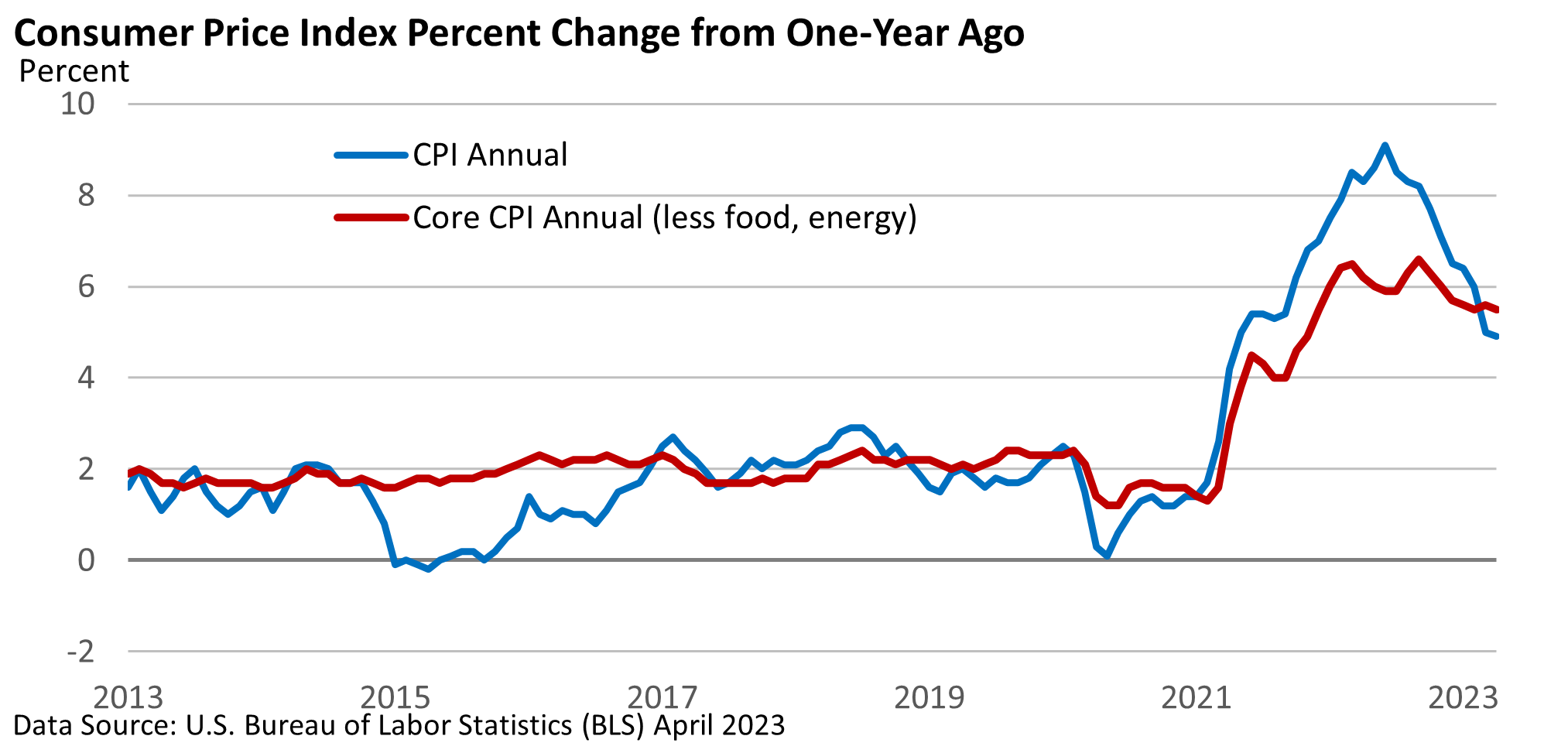
The results aligned with expectations, raising optimism that the Federal Reserve might not hike interest rates at its June meeting.
That’s a possibility, as the Fed has left its options open for June.
While fears of a recession are high and some cautiously encouraging internals were buried in the report, the Fed has yet to approach its goal of getting inflation back to 2%.
In Fed Chief Powell’s opening statement at his May 3 press conference, he was pretty emphatic about snuffing out inflation. Twice he said the Fed remains “strongly committed” to getting inflation back to 2%— not just committed but ‘strongly’ committed.
The rhetoric was generally in line with remarks last year, suggesting the Fed isn’t finished. But he also said the Fed is “much closer to the end of this (rate hikes) than to the beginning.”
Besides, the banking crisis continues to simmer, and additional rate increases could further pressure regional banks that are struggling under the weight of negative psychology.
Minus the uncertainties swirling around the regional banks, more rate hikes would probably be in the pipeline.
Inflation is gradually easing, but getting to 2% without a recession seems like a long shot. As the Wall Street Journal recently pointed out, some firms are taking advantage of today’s inflationary environment and boosting prices above rising costs simply because they can.
That could continue unless the economy slips into a recession, wages gains evaporate, and companies lose the ability to aggressively raise prices.




