
The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) reported that first quarter Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which is the broadest measure of economic activity, fell at an annualized pace of 0.3%.
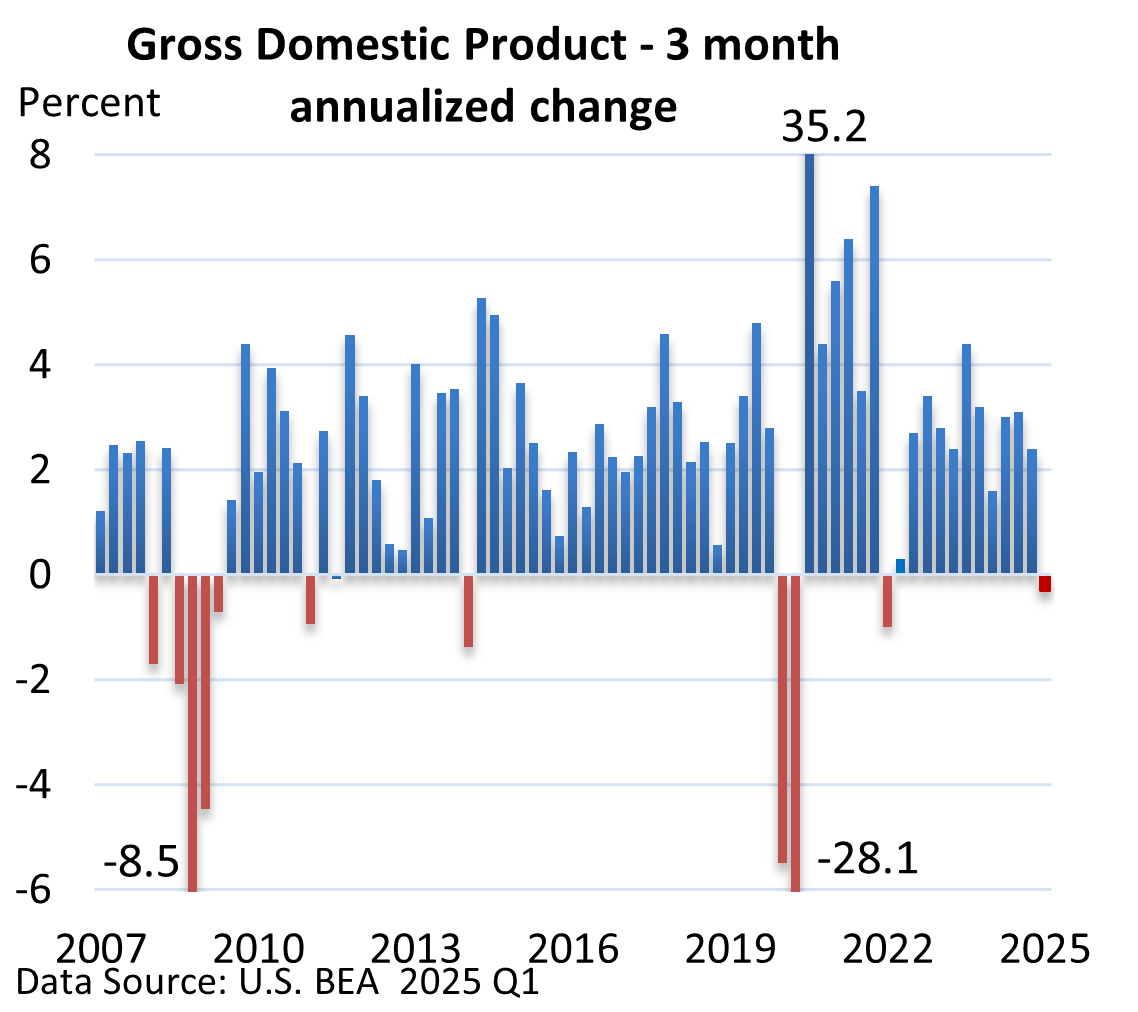
Yet, a closer look reveals that the economy didn’t shrink in Q1.
What happened? Businesses rushed to stockpile goods ahead of tariffs, which depressed GDP. Let’s explain with a simple example.
If Americans purchased 1,000 toasters in Q4 and companies imported 100 toasters from abroad, GDP, which measures domestic production, would effectively count 900 toasters, as 100 were imported.
If Americans purchased 1,100 toasters in Q1 and companies, anticipating tariffs, imported 300 toasters, this results in a net increase of 800 toasters, down from 900 in the previous period.
Although consumer purchases rose by 100, the spike in imports weighed on GDP.
In Q1, imports jumped a record 41% (quarterly GDP records began in 1947), which shaved a staggering five percentage points off GDP, according to the U.S. BEA.
However, companies did not sell the massive influx of imports, leaving some to accumulate in warehouses across the country.
This surge in inventories contributed more than two percentage points to GDP.
Why? Inventories act as a balancing figure—when they increase, it adds to GDP; when they decline, it detracts from GDP.
Net the two categories, and GDP would have expanded in the first quarter. We might expect some of this to unwind in the second and third quarters.
But given the distortions in trade data, the economy during the first three months of the year was healthier than the headline number suggested.
One final remark: even amid the high level of economic uncertainty, stocks have recently mounted an impressive rally, with the S&P 500 rising for nine straight days (MarketWatch data).
Despite higher tariffs that remain in place, investors are hopeful that the delay in the most stringent levies, coupled with the ‘hope’ of new trade agreements, will enable the economy to sidestep a recession.




